Answer B is Incorrect, Try Again
![]()
Answer B is Incorrect, Try Again
![]()
Answer C is Incorrect, Try Again
| A standard briefing is the most complete report and provides the overall weather picture. This type of briefing should be obtained prior to the departure of any flight and should be used during flight planning. |
| A standard briefing is the most complete report and provides the overall weather picture. This type of briefing should be obtained prior to the departure of any flight and should be used during flight planning. |
| "Zero sink" means that upward currents are just strong enough to hold altitude but not to climb... There is no point in trying to soar until weather conditions favor vertical speeds greater than the minimum sink rate of the aircraft. |
| An "outlook" briefing will be provided when the proposed departure is 6 hours or more from the time of the briefing. Briefing will be limited to applicable forecast data needed for the proposed flight. |
| When requesting a briefing, pilots should identify themselves as pilots and give clear and concise facts about their flight: 1. Type of flight (VFR or IFR) 2. Aircraft identification or pilotís name 3. Aircraft type 4. Departure point 5. Proposed time of departure 6. Flight altitude(s) 7. Route of flight 8. Destination 9. Estimated time en route (ETE) |
| TWEB Generally, the broadcast contains route-oriented data with specially prepared NWS forecasts, Inflight Advisories, and winds aloft plus preselected current information. |
| The transcribed weather broadcast (TWEB) provides continuous aeronautical and meteorological information on low/medium frequency (L/MF) and very high frequency (VHF) omni-directional radio range (VOR) facilities. The synopsis and route forecasts are prepared specifically for the TWEB by WFOs. |
| An "abbreviated" briefing will be provided at the userís request: 1. To supplement mass disseminated data. 2. To update a previous briefing. 3. To request that the briefing be limited to specific information. |
| An "outlook" briefing will be provided when the proposed departure is 6 hours or more from the time of the briefing. Briefing will be limited to applicable forecast data needed for the proposed flight. |
| For aviation purposes, the ceiling is defined as the height (AGL) of the lowest broken or overcast layer aloft or vertical visibility into an obscuration. |
| The wind element is reported as a five-digit group (six digits if speed is over 99 knots). The first three digits are the direction from which the wind is blowing in tens of degrees referenced to true north. The next two digits are the average speed in knots, or if over 99 knots, the next three digits. If the wind is gusty, G denoting gust is reported after the speed followed by the highest gust reported. The abbreviation KT is appended to denote the use of knots for wind speed. |
| The contraction RMK follows the altimeter in the body and precedes the actual remarks. Time entries will be shown as minutes past the hour if the time reported occurs during the same hour the observation is taken. If the hour is different, hours and minutes will be shown. |
| Prevailing visibility is reported in statute miles followed by a space, fractions of statute miles, as needed, and the letters SM. |
| Prevailing visibility is reported in statute miles followed by a space, fractions of statute miles, as needed, and the letters SM. |
| /TA Temperature (Celsius): If below zero, prefix with an "M." /WV Wind: Direction from which the wind is blowing coded in tens of degrees using three digits. The wind speed shall be entered as a two- or three-digit group. /TB Turbulence: Include altitude only if different from FL. /IC Icing: /RM Remarks: Use free form to clarify the report putting hazardous elements first. |
| For aviation purposes, the ceiling is defined as the height (AGL) of the lowest broken or overcast layer aloft or vertical visibility into an obscuration. |
| /TA Temperature (Celsius): If below zero, prefix with an "M." /WV Wind: Direction from which the wind is blowing coded in tens of degrees using three digits. The wind speed shall be entered as a two- or three-digit group. /TB Turbulence: Include altitude only if different from FL. /IC Icing: /RM Remarks: Use free form to clarify the report putting hazardous elements first. |
| /TA Temperature (Celsius): If below zero, prefix with an "M." /WV Wind: Direction from which the wind is blowing coded in tens of degrees using three digits. The wind speed shall be entered as a two- or three-digit group. /TB Turbulence: Include altitude only if different from FL. /IC Icing: /RM Remarks: Use free form to clarify the report putting hazardous elements first. |
| AIRMETs are intended for dissemination to all pilots in the preflight and en route phase of flight to enhance safety. |
| Convective SIGMETs are issued for any of the following: 1. Severe thunderstorm due to: a. surface winds >= 50 knots; b. hail at the surface >= 3/4 inches in diameter; c. tornadoes; 2. Embedded thunderstorms; 3. A line of thunderstorms; 4. Thunderstorms >= VIP level 4 affecting 40% or more of an area at least 3000 square miles. |
| A SIGMET advises of non-convective weather that is potentially hazardous to all aircraft... SIGMETs are issued when the following occur or are expected to occur: 1. Severe icing not associated with thunderstorms; 2. Severe or extreme turbulence or clear air turbulence (CAT) not associated with thunderstorms; 3. Duststorms, sandstorms, or volcanic ash lowering ... visibilities to below three miles; 4. Volcanic ash. |
| A SIGMET advises of non-convective weather that is potentially hazardous to all aircraft... SIGMETs are issued when the following occur or are expected to occur: 1. Severe icing not associated with thunderstorms; 2. Severe or extreme turbulence or clear air turbulence (CAT) not associated with thunderstorms; 3. Duststorms, sandstorms, or volcanic ash lowering ... visibilities to below three miles; 4. Volcanic ash. |
| A six-digit group shows wind direction, in reference to true north, wind speed in knots, and temperature in degrees Celsius. If a wind direction is coded between 51 and 86, subtract 50 from the wind direction and add 100 knots to the wind speed. When the forecast speed is less than 5 knots, the coded group is "9900" and read, "LIGHT AND VARIABLE." |
| A six-digit group shows wind direction, in reference to true north, wind speed in knots, and temperature in degrees Celsius. If a wind direction is coded between 51 and 86, subtract 50 from the wind direction and add 100 knots to the wind speed. When the forecast speed is less than 5 knots, the coded group is "9900" and read, "LIGHT AND VARIABLE." |
| A six-digit group shows wind direction, in reference to true north, wind speed in knots, and temperature in degrees Celsius. If a wind direction is coded between 51 and 86, subtract 50 from the wind direction and add 100 knots to the wind speed. When the forecast speed is less than 5 knots, the coded group is "9900" and read, "LIGHT AND VARIABLE." |
| The valid period of the forecast is a two-digit date followed by the two-digit beginning and two-digit ending hours in UTC. Routine TAFs are valid for 24 hours and are issued four times daily at 0000Z, 0600Z, 1200Z, and 1800Z. |
| The BECMG group is used when a gradual change in conditions is expected over a period not to exceed 2 hours. The time period when the change is expected to occur is a four-digit group containing the beginning and ending hours of the change that follows the BECMG indicator. |
| Forecasted visibility greater than 6 statute miles is indicated by coding P6SM. |
| Cumulonimbus clouds (CB) are the only cloud type forecasted in TAFs. |
| Convective SIGMETs are issued for any of the following: 1. Severe thunderstorm due to: a. surface winds >= 50 knots; b. hail at the surface >= 3/4 inches in diameter; c. tornadoes; 2. Embedded thunderstorms; 3. A line of thunderstorms; 4. Thunderstorms >= VIP level 4 affecting 40% or more of an area at least 3000 square miles. |
| Examples: TSRA indicates thunderstorm with moderate rain. +SHRA indicates heavy rainshowers. -FZRA indicates light freezing rain. |
| The BECMG group is used when a gradual change in conditions is expected over a period not to exceed 2 hours. The time period when the change is expected to occur is a four-digit group containing the beginning and ending hours of the change that follows the BECMG indicator. |
| Calm winds are encoded as 00000KT. A variable wind is encoded as VRB when wind direction fluctuates due to convective activity or low wind speeds (3 knots or less). |
| The BECMG group is used when a gradual change in conditions is expected over a period not to exceed 2 hours. The time period when the change is expected to occur is a four-digit group containing the beginning and ending hours of the change that follows the BECMG indicator. |
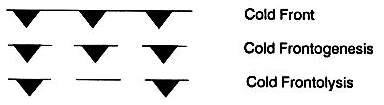 AC00-6A p71 - As adjacent air masses modify and as temperature and pressure differences equalize across a front, the front dissipates. This process (is) frontolysis. Frontogenesis is the generation of a front. AC00-6A p71 - As adjacent air masses modify and as temperature and pressure differences equalize across a front, the front dissipates. This process (is) frontolysis. Frontogenesis is the generation of a front.
|
| Cloud height above ground level (AGL) is entered under the station circle in hundreds of feet. If total sky cover at a station is scattered, the cloud height entered is the base of the lowest scattered cloud layer. If total sky cover is broken or greater at a station, the cloud height entered is the lowest broken or overcast cloud layer. A totally obscured sky is shown by the sky cover symbol "X" and is accompanied by the height entry of the vertical visibility into the obscuration. A partially obscured sky with clouds above will have a cloud height entry for the cloud layer. |
| The weather depiction chart is an ideal place to begin preparing for a weather briefing and flight planning. From this chart, one can get a "birdís eye" view of areas of favorable and adverse weather conditions for chart time. |
| IFR = Ceiling less than 1,000 feet and/or visibility less than 3 miles; MVFR (Marginal VFR) = Ceiling 1,000 to 3,000 feet inclusive and/or visibility 3 to 5 miles inclusive; VFR = No ceiling or ceiling greater than 3,000 feet and visibility greater than 5 miles. |
| This chart displays areas of precipitation as well as information about type, intensity, configuration, coverage, echo top, and cell movement of precipitation. Severe weather watches are plotted if they are in effect when the chart is valid. |
| This chart displays areas of precipitation as well as information about type, intensity, configuration, coverage, echo top, and cell movement of precipitation. Severe weather watches are plotted if they are in effect when the chart is valid. |
| Individual cell movement is indicated by an arrow with the speed in knots entered as a number at the top of the arrow head. Little movement is identified by LM. Line or area movement is no longer indicated on the chart. |
| Heights are displayed in hundreds of feet MSL and should be considered only as approximations because of radar limitations. Tops are entered above a short line, with the top height displayed being the highest in the indicated area. Absence of a figure below the line indicates that the echo base is at or near the surface. |
| Turbulence intensities are identified by symbols. The vertical extent of turbulence layers is specified by top and base heights in hundreds of feet. Height values are relative to MSL with the top and base heights separated by a line. A top height of "240" indicates turbulence at or above 24,000 feet. The base height is omitted where turbulence reaches the surface. For example, "080/ " identifies a turbulence layer from the surface to 8,000 feet MSL. |
| The significant weather panels display forecast weather flying categories, freezing levels, and turbulence for the layer surface to FL240. A legend on the chart illustrates symbols and criteria used for these conditions. |
| Continuous precipitation is a dominant and widespread event and, therefore, shaded. Intermittent precipitation is a periodic and patchy event and unshaded. |
| Freezing levels aloft are depicted by thin, short dashed lines. Lines are drawn at 4,000-foot intervals beginning at 4,000 feet and labeled in hundreds of feet. |
| The significant weather panels display forecast weather flying categories, freezing levels, and turbulence for the layer surface to FL240. A legend on the chart illustrates symbols and criteria used for these conditions. |
| ATIS is the continuous broadcast of recorded non-control information in selected high activity terminal areas. |
| EFAS is a service specifically designed to provide en route aircraft with timely and meaningful weather advisories. EFAS provides communications capabilities for aircraft flying at 5,000 feet AGL to 17,500 feet MSL on 122.0 MHz. Contact flight watch by using the name of the ARTCC facility serving the area .., followed by your aircraft identification, and the name of the nearest VOR. |
| EFAS is a service specifically designed to provide en route aircraft with timely and meaningful weather advisories. EFAS provides communications capabilities for aircraft flying at 5,000 feet AGL to 17,500 feet MSL on 122.0 MHz. Contact flight watch by using the name of the ARTCC facility serving the area .., followed by your aircraft identification, and the name of the nearest VOR. |
| EFAS is a service specifically designed to provide en route aircraft with timely and meaningful weather advisories. EFAS provides communications capabilities for aircraft flying at 5,000 feet AGL to 17,500 feet MSL on 122.0 MHz. Contact flight watch by using the name of the ARTCC facility serving the area .., followed by your aircraft identification, and the name of the nearest VOR. |
|
| Larger negative numbers favor stronger conditions, while values of 0 to -2 may produce few or no thermals. |
| Larger negative numbers favor stronger conditions, while values of 0 to -2 may produce few or no thermals. |
| The forecast visibility is given in statute miles and may be in whole numbers or fractions. If the forecast is greater than 6 miles, it will be coded as "P6SM." |
| The common EFAS frequency, 122.0 MHz, is established for pilots of aircraft flying between 5,000 feet AGL and 17,500 feet MSL. |
| BR is used to indicate mist restricting visibility and is used only when the visibility is from 5/8 mile to 6 miles. FG is used to indicate fog restricting visibility and is used only when visibility is less than 5/8 mile. |
| Each TAF is valid for a 24-hour time period, and is updated four times a day at 0000Z, 0600Z, 1200Z, and 1800Z. |
| Winds are reported with five digits (14021) unless the speed is greater than 99 knots...The first three digits indicate the direction...If the wind is variable, it is reported as "VRB." The last two (or three) digits indicate the speed of the wind in knots. |
| If thermals are to develop, the lapse rate must become equal to or greater than the dry adiabatic rate of cooling - that is, the line representing the lapse rate must slope parallel to or slope more than the dry adiabats. |
| If thermals are to develop, the lapse rate must become equal to or greater than the dry adiabatic rate of cooling - that is, the line representing the lapse rate must slope parallel to or slope more than the dry adiabats. |
| HIWAS: This is a continuous broadcast of inflight weather advisories including summarized AWW, SIGMET's, Convective SIGMET's, CWA's, AIRMET's, and urgent PIREP's. |
| A SIGMET advises of non-convective weather that is potentially hazardous to all aircraft... SIGMETs are issued when the following occur or are expected to occur: 1. Severe icing not associated with thunderstorms; 2. Severe or extreme turbulence or clear air turbulence (CAT) not associated with thunderstorms; 3. Duststorms, sandstorms, or volcanic ash lowering ... visibilities to below three miles; 4. Volcanic ash. |
| Convective SIGMETs are issued for any of the following: 1. Severe thunderstorm due to: a. surface winds >= 50 knots; b. hail at the surface >= 3/4 inches in diameter; c. tornadoes; 2. Embedded thunderstorms; 3. A line of thunderstorms; 4. Thunderstorms >= VIP level 4 affecting 40% or more of an area at least 3000 square miles. |
| Isobars are solid lines depicting the sea level pressure pattern and are usually spaced at intervals of 4 millibar (mb). |
| The surface analysis chart provides a ready means of locating pressure systems and fronts. It also gives an overview of winds, temperatures, and dew point temperatures at chart time. |
| Cloud height above ground level (AGL) is entered under the station circle in hundreds of feet. If total sky cover at a station is scattered, the cloud height entered is the base of the lowest scattered cloud layer. If total sky cover is broken or greater at a station, the cloud height entered is the lowest broken or overcast cloud layer. A totally obscured sky is shown by the sky cover symbol "X" and is accompanied by the height entry of the vertical visibility into the obscuration. A partially obscured sky with clouds above will have a cloud height entry for the cloud layer. |
| This chart displays areas of precipitation as well as information about type, intensity, configuration, coverage, echo top, and cell movement of precipitation. Severe weather watches are plotted if they are in effect when the chart is valid. |
| A six-digit group shows wind direction, in reference to true north, wind speed in knots, and temperature in degrees Celsius. If a wind direction is coded between 51 and 86, subtract 50 from the wind direction and add 100 knots to the wind speed. When the forecast speed is less than 5 knots, the coded group is "9900" and read, "LIGHT AND VARIABLE." |
| Significant weather prognostic charts (progs) portray forecasts of selected weather conditions at specified valid times. Each valid time is the time at which the forecast conditions are expected to occur. |
| The low-level significant weather prog chart is a day 1 forecast of significant weather for the conterminous United States. Weather information provided pertains to the layer from surface to FL240 (400 mbs.) |
| AIRMET's (WA's) may be of significance to any pilot or aircraft operator and are issued for all domestic airspace ... for the following weather phenomena which are potentially hazardous to aircraft: 1. Moderate icing. 2. Moderate turbulence. 3. Sustained winds of 30 knots or more at the surface. 4. Widespread area of ceilings less than 1,000 feet and/or visibility less than three miles. 5. Extensive mountain obscurement. |
| Weather Advisory Broadcasts: ARTCC's broadcast a Severe Weather Forecast Alert (AWW), Convective SIGMET, SIGMET, or CWA alert once on all frequencies, except emergency, when any part of the area described is within 150 miles of the airspace under their jurisdiction. |
| For aviation purposes, the ceiling is defined as the height (AGL) of the lowest broken or overcast layer aloft or vertical visibility into an obscuration. |
| Whenever a wind shift occurs, "WSHFT" will be included in remarks followed by the time the wind shift began, e.g., WSHFT 30 FROPA "Wind shift at three zero due to frontal passage." |
| TIBS, provided by automated flight service stations (AFSS's) is a continuous recording of meteorological and aeronautical information, available by telephone. |
| TWEB: Generally, the broadcast contains route-oriented data with specially prepared NWS forecasts, Inflight Advisories, and winds aloft plus preselected current information, such as weather reports (METAR/SPECI), NOTAM's, and special notices. |
| The LLWAS provides wind data and software processes to detect the presence of hazardous wind shear and microbursts in the vicinity of an airport. |
| SIGMET's (WS's) within the conterminous U.S. are issued by the Aviation Weather Center (AWC) when the following phenomena occur or are expected to occur: 1. Severe or extreme turbulence or clear air turbulence (CAT) not associated with thunderstorms. 2. Severe icing not associated with thunderstorms. 3. Duststorms, sandstorms, or volcanic ash lowering surface or inflight visibilities to below three miles. 4. Volcanic eruption. |
| If thermals are to develop, the lapse rate must become equal to or greater than the dry adiabatic rate of cooling - that is, the line representing the lapse rate must slope parallel to or slope more than the dry adiabats. |
| The wind element is reported as a five-digit group (six digits if speed is over 99 knots). The first three digits are the direction from which the wind is blowing in tens of degrees referenced to true north. The next two digits are the average speed in knots, or if over 99 knots, the next three digits. If the wind is gusty, G denoting gust is reported after the speed followed by the highest gust reported. The abbreviation KT is appended to denote the use of knots for wind speed. |
| Temperature/dew point are reported in a two-digit form in whole degrees Celsius separated by a solidus (/). Temperatures below zero are prefixed with M. |
| The maintenance flag ($) is automatically appended to the observation to indicate that the site may be in need of maintenance. |
| BR is used to indicate mist restricting visibility and is used only when the visibility is from 5/8 mile to 6 miles. FG is used to indicate fog restricting visibility and is used only when visibility is less than 5/8 mile. |
| /SK Sky cover: Describes cloud amount, height of cloud bases, and height of cloud tops. If unknown, use UNKN. Ex: /SK SCT040-TOP080 |
| The valid period of the forecast is a two-digit date followed by the two-digit beginning and two-digit ending hours in UTC. Routine TAFs are valid for 24 hours and are issued four times daily at 0000Z, 0600Z, 1200Z, and 1800Z. |
| A SIGMET advises of non-convective weather that is potentially hazardous to all aircraft... SIGMETs are issued when the following occur or are expected to occur: 1. Severe icing not associated with thunderstorms; 2. Severe or extreme turbulence or clear air turbulence (CAT) not associated with thunderstorms; 3. Duststorms, sandstorms, or volcanic ash lowering ... visibilities to below three miles; 4. Volcanic ash. |
| There are three AIRMETs - Sierra, Tango, and Zulu. AIRMET Sierra describes IFR conditions and/or extensive mountain obscurations. AIRMET Tango describes moderate turbulence, sustained surface winds of 30 knots or greater, and/or nonconvective low-level wind shear. AIRMET Zulu describes moderate icing and provides freezing level heights. |
| All heights are in hundreds of feet. |
| There are three AIRMETs - Sierra, Tango, and Zulu. AIRMET Sierra describes IFR conditions and/or extensive mountain obscurations. AIRMET Tango describes moderate turbulence, sustained surface winds of 30 knots or greater, and/or nonconvective low-level wind shear. AIRMET Zulu describes moderate icing and provides freezing level heights. |
| The height into an indefinite ceiling is preceded with VV followed by three digits indicating the vertical visibility in hundreds of feet above ground level. |
| The synopsis is a brief summary of the location and movements of fronts, pressure systems, and other circulation features for an 18-hour period. |
| A three-digit number near a front classifies it as to type, intensity, and character. |
 AC00-6A p71 - As adjacent air masses modify and as temperature and pressure differences equalize across a front, the front dissipates. This process (is) frontolysis. Frontogenesis is the generation of a front. AC00-6A p71 - As adjacent air masses modify and as temperature and pressure differences equalize across a front, the front dissipates. This process (is) frontolysis. Frontogenesis is the generation of a front.
|
| The weather depiction chart is an ideal place to begin preparing for a weather briefing and flight planning. From this chart, one can get a "birdís eye" view of areas of favorable and adverse weather conditions for chart time. |
|
| A positive LI means a lifted surface parcel of air is stable. The more positive the LI, the more stable the air. Large positive values (+8 or greater) would indicate very stable air. |
| The significant weather panels display forecast weather flying categories, freezing levels, and turbulence for the layer surface to FL240. A legend on the chart illustrates symbols and criteria used for these conditions. |
| The ceiling/sky condition, visibility, and obstructions to vision may be omitted from the ATIS broadcast if the ceiling is above 5,000 feet and the visibility is more than 5 miles. |
